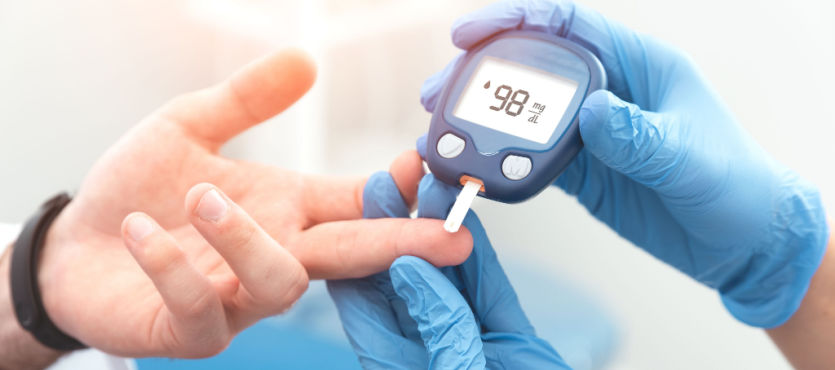
You can have a normal and active lifestyle if you proactively take control of your diabetes care. However, it is still important to go for your regular checkups and tests. These appointments will tell you if your effort to curb the impact of diabetes on your body is working or not and if there is anything that you may need to change.
Visit Your Doctor
It is imperative that you see your doctor every 3 to 6 months. During the visit, your doctor will take a report of your blood pressure, weight, and your feet. You should also make an appointment to see your dentist every 6 months.
Eye Exams
You should see your eye doctor (called an ophthalmologist) at least once a year. You may need to visit often if you are having eye problems due to diabetes.
Foot Exams
Your doctor should take a report of the pulses in your feet and check your reflexes at least once a year. They should also look for infections, sore spots, and calluses. If you have recovered from foot ulcers in the past, you should see your doctor every 3 to 6 months.
Routine Tests
Every diabetes patient has to get an HbA1C test which will confirm the average amount of sugar in their blood over the past 3 months. In simple words, it tells you how well you are controlling your diabetes. While the normal level is less than 6%, every diabetes patient should have an HbA1C of less than 7%.
Cholesterol Test
A cholesterol test will give you an idea of how much cholesterol and triglycerides are present in your blood. The test is conducted on an empty stomach (after not eating overnight) and adults should get this test done at least once a year. If you have been diagnosed with high cholesterol, you might need to undergo this test more than once a year.
Kidney Tests
For patients with diabetes, a kidney test is mainly conducted to check for the presence of albumin in the urine. Those with kidney damage will have a higher amount of albumin present in their urine. Although, there could be other reasons behind higher levels of albumin. Your doctor should also perform blood tests to assess the condition of your kidneys.
Type I Diet:
If you have type 1 diabetes, it is better to know your carbohydrate intake with every meal. This will play a major role in deciding how much insulin you should be taking to maintain blood sugar level. Although not as rapid as carbohydrates, protein and fat also have an impact on blood glucose levels. To keep your diabetes under control, you should aim for optimal balance between carbohydrate intake, insulin, and physical activity. If any of these areas are overlooked, it can result in wide swings in your blood glucose levels. If you have type 1 diabetes and you take a set amount of insulin, your carbohydrate intake and physical activity should be consistent every day.
Meal Planning
One of the most significant aspects of controlling diabetes is meal planning. You should work closely with your doctor and dietician to come up with a balanced and healthy diet that helps you maintain your blood sugar levels while meeting your daily nutritional needs. Be it for you or your child, the meal plan should focus on giving you the right amount of calories to maintain a healthy body weight. There needs to be a subtle balance between your food and insulin intake. Any food that you eat increases your blood glucose levels, whereas insulin decreases blood sugar. Here are some tips to keep in mind when coming up with a meal plan:
- Make a list of foods that you or your child eat daily. Work with your doctor and dietician to devise a meal plan that revolves around these foods. Be sure to incorporate insulin in your meal plan and time your meals optimally.
- Consistency is key when it comes to controlling diabetes. The time of the day you eat your meals and snacks should remain the same every day. Be sure to not skip any meals as this can affect your blood glucose levels and insulin intake.
- To maintain an optimal carbohydrate intake, read the labels on food items that you or your child are consuming.
- Take the right amount of insulin at the same time each day, as prescribed by your doctor.
Diabetes patients should keep a close watch on their blood glucose levels. Adjust the insulin intake depending on your blood glucose levels and food intake, as directed by your doctor. Having diabetes does not mean that you have to give up on certain foods entirely, but it does mean moderating the amount and type of foods that you eat daily. Choose foods that will help you maintain healthy weight while keeping your blood sugar levels in check.